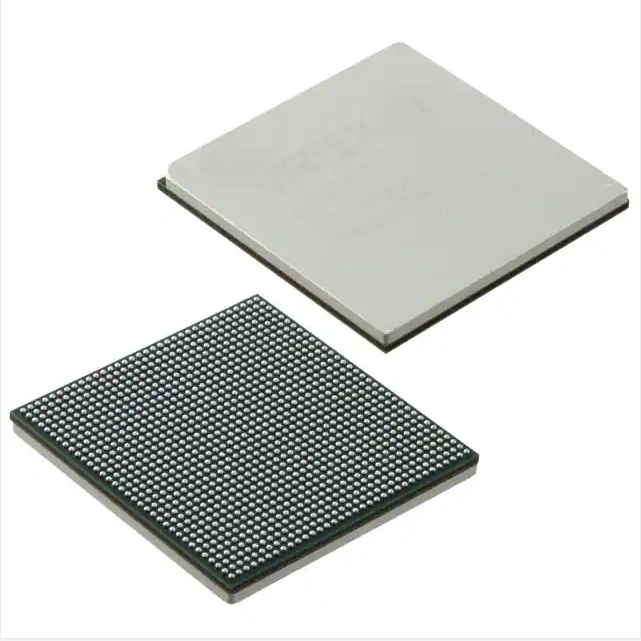
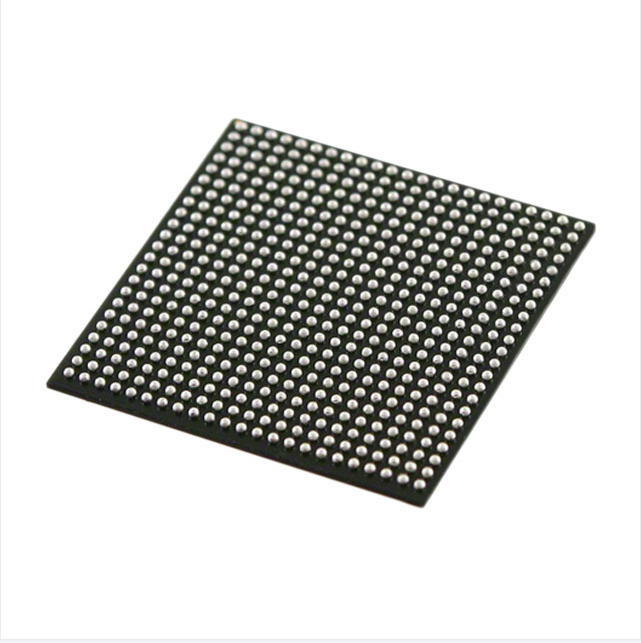
EP2S15F484C3N 484-FBGA (23×23) integrated circuit IC FPGA 342 I/O 484FBGA integrated electronics
Product Attributes
| TYPE | DESCRIPTION |
| Category | Integrated Circuits (ICs) Embedded FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Array) |
| Mfr | Intel |
| Series | Stratix® II |
| Package | Tray |
| Standard Package | 60 |
| Product Status | Obsolete |
| Number of LABs/CLBs | 780 |
| Number of Logic Elements/Cells | 15600 |
| Total RAM Bits | 419328 |
| Number of I/O | 342 |
| Voltage – Supply | 1.15V ~ 1.25V |
| Mounting Type | Surface Mount |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C ~ 85°C (TJ) |
| Package / Case | 484-BBGA |
| Supplier Device Package | 484-FBGA (23×23) |
| Base Product Number | EP2S15 |
Intel Chipsets
The chipset is the heart of the circuitry that makes up the motherboard. In a certain sense, it determines the level and class of the motherboard. It is the collective name for the “Southbridge” and “Northbridge”, the chipset that maximizes the integration of previously complex circuits and components into a few chips. The Intel chipset is specifically designed for Intel processors and is used to connect the CPU to other devices such as memory and graphics cards.
If the central processing unit (CPU) is the brain of the entire computer system, then the chipset will be the heart of the entire body. The motherboard, the chipset pretty much determines the functionality of this motherboard, which in turn affects the performance of the entire computer system, the chipset is the soul of the motherboard. The performance of the chipset determines the performance of the motherboard.
Manufacturers
So far, the manufacturers that can produce chipsets are VIA (VIA, Taiwan), SiS (SiS, Taiwan), ULI (ULI, Taiwan), Ali (Yangzhi, Taiwan), AMD (Supermicro, USA), NVIDIA (NVIDIA, USA), ATI (ATI, Canada), ServerWorks (USA), IBM (USA), HP (USA) and many others. The chipsets of Intel and AMD and NVIDIA are the most common. On the Intel platform for desktops, Intel and AMD’s chipsets have the largest market share and a complete product line, with high, mid, and low-end and integrated products, while other chipset manufacturers VIA, SIS, ULI, and NVIDIA together have a relatively small market share. VIA used to have the largest market share of AMD platform chipsets and has taken a lot of market share from VIA and is now the largest chipset vendor on the AMD platform, while SIS and ULI are still playing supporting roles, mainly in the mid-range, low-end and integrated areas.
The market share of SIS and ULI continues to play a supporting role, mainly in the mid-range, low-end and integrated segments. In notebooks, the Intel platform has an absolute advantage, so Intel’s notebook chipsets also occupy the largest market share, while other manufacturers can only play a supporting role and design products for the AMD platform, which has a very small market share. In terms of servers/workstations, the Intel platform is dominant, Intel’s own server/workstation chipsets occupy the majority of the market share, but in the field of high-end Intel-based multi-channel servers, IBM and HP have an absolute advantage, for example, IBM’s XA32 and HP’s F8 are very good high-end multi-channel server chipset products. For example, IBM’s XA32 and HP’s F8 are excellent high-end multi-channel server chipset products, but they are only used in the company’s server products and not too famous; while AMD server/workstation platforms are mainly used AMD’s chipset products due to their small market share, and ULI has been acquired by NVIDIA, which is also very likely to withdraw from the chipset market. In short, INTEL has unparalleled strength in the chipset field.
Classification naming
Intel chipsets are often divided into series, such as 845, 865, 915, 945, 975, etc., the same series of various models with letters to distinguish, naming certain rules, master these rules, you can quickly understand to a certain extent the positioning and characteristics of the chipset.
A, from 845 series to 915 series before
PE is the mainstream version, without integrated graphics, supporting the mainstream FSB and memory at the time, and supporting AGP slots.
E is not a simplified version but should be an evolutionary version. What is special is that the only one with the E suffix is the 845E, whose relative to the 845D is an increase in 533MHz FSB support, while relative to the 845G and the like is an increase in support for ECC memory, so the 845E is commonly used in entry-level servers.
The G is the mainstream integrated graphics chipset and supports the AGP slot, the rest of the parameters are similar to the PE.
The GV and GL are simplified versions of the integrated graphics chipset and do not support AGP slots, while the GV is the same as the G and the GL is somewhat smaller.
The GE is an evolution of the integrated graphics chipset and also supports the AGP slot.
There are two types of P, one is an enhanced version, such as the 875P; the other is a simplified version, such as the 865P.
II. 915 series and beyond
P is the mainstream version, without integrated graphics, supporting the mainstream FSB and memory of the time, and supporting the PCI-E X16 slot.
The PL is a simplified version compared to the P. It has been scaled down in terms of FSB and memory support, with no integrated graphics, but also supports PCI-E X16.
The G is the mainstream integrated graphics chipset and supports the PCI-E X16 slot, the rest of the parameters are similar to the P.
The GV and GL are simplified versions of the integrated graphics chipset and do not support PCI-E X16 slots, while the GV is the same as the G and the GL has been scaled down.
The X and XE are enhanced versions of the P, with no integrated graphics and support for the PCI-E X16 slot.
In general, there are no strict rules for the naming of Intel chipsets, but broadly speaking, it is the above situation.
Third, from the 965 series onwards, Intel adopts new naming rules
Changing the letters of the chipset function from a suffix to a prefix. For example, P965 and Q965 and so on. And subdivided for different user groups!
P is the mainstream chipset version for individual users, with no integrated graphics, support for mainstream FSB and memory, and support for PCI-E X16 slots.
The G is the mainstream integrated graphics chipset for individual users, supporting PCI-E X16 slots and the rest of the parameters are similar to the P series.